AI-Driven. Tech-Enhanced.
L everaging AI tools and technologies for demand forecasting, inventory optimization, cost reduction and driving business growth. We deliver cutting-edge solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our end-to-end services include integration and deployment, automated monitoring and maintenance, scalable infrastructure management, and ensuring your models are always performing at their best.
Data Q&A Copilot
Convert plain English to optimized, safe SQL with schema learning.

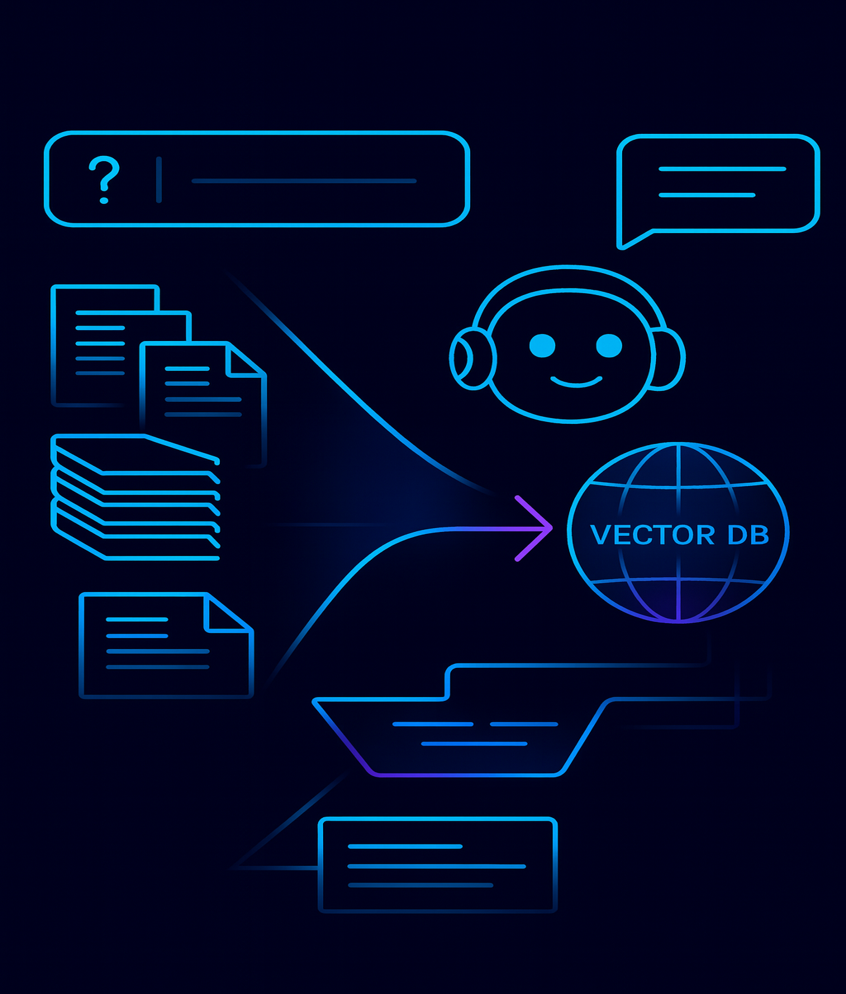
RAG Knowledge Chatbots
Empower enterprise data with natural Q&A over your docs.
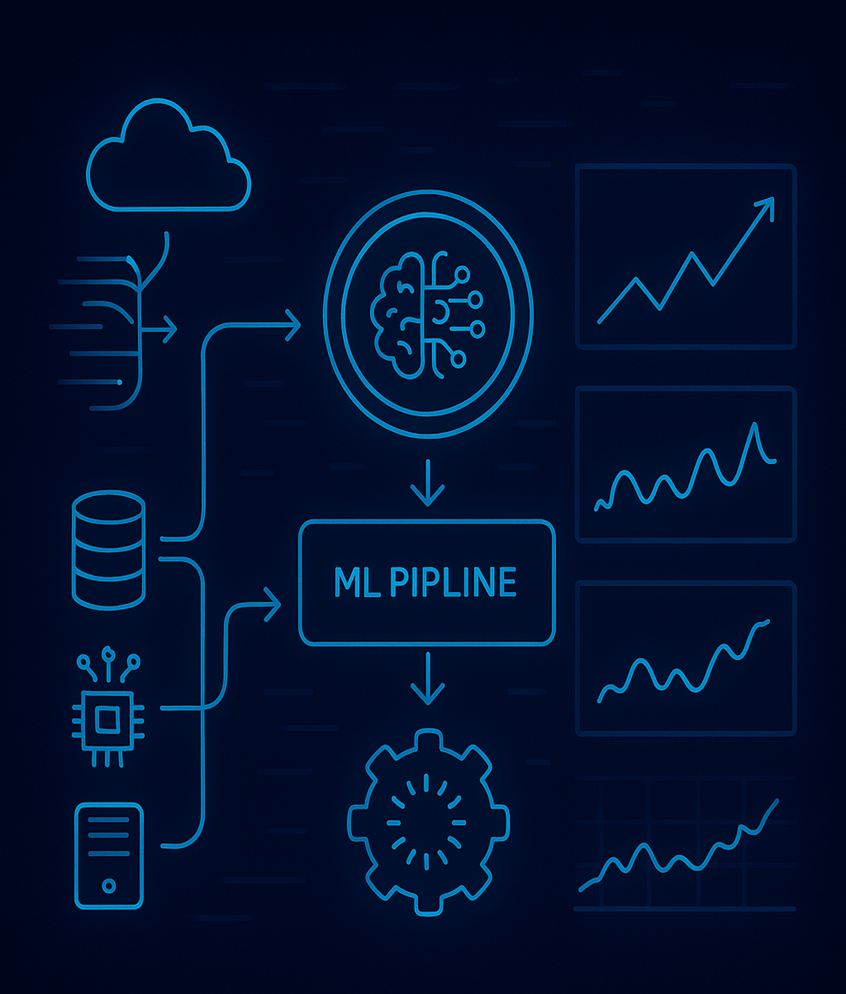
Predictive Insights Engine
Forecast trends using ML pipelines and real-time data.
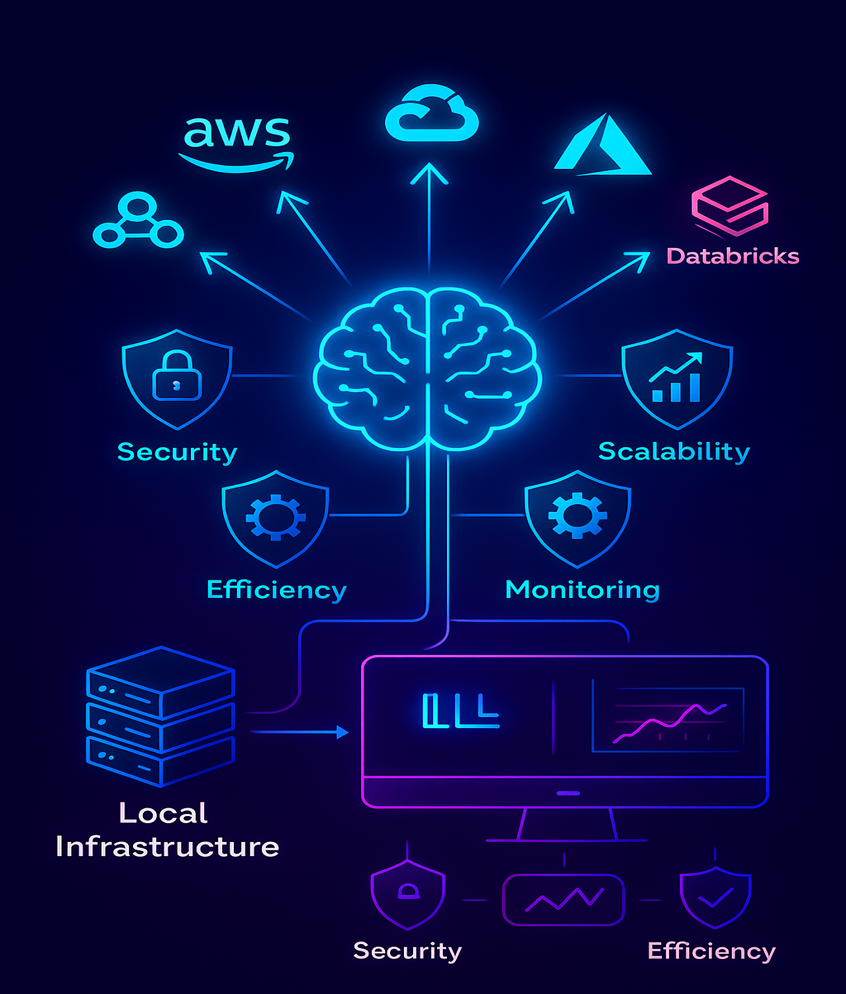
AI Infrastructure on Cloud
Deploy LLMs on AWS, GCP, or Azure with best practices.
AI Ops Automation
Monitor, retrain, and version models with automated workflows.

Dynamic Pricing Models
Optimize pricing with demand-aware ML and A/B testing.

Research & Development
Prototype new AI ideas, evaluate models, and validate POCs fast.

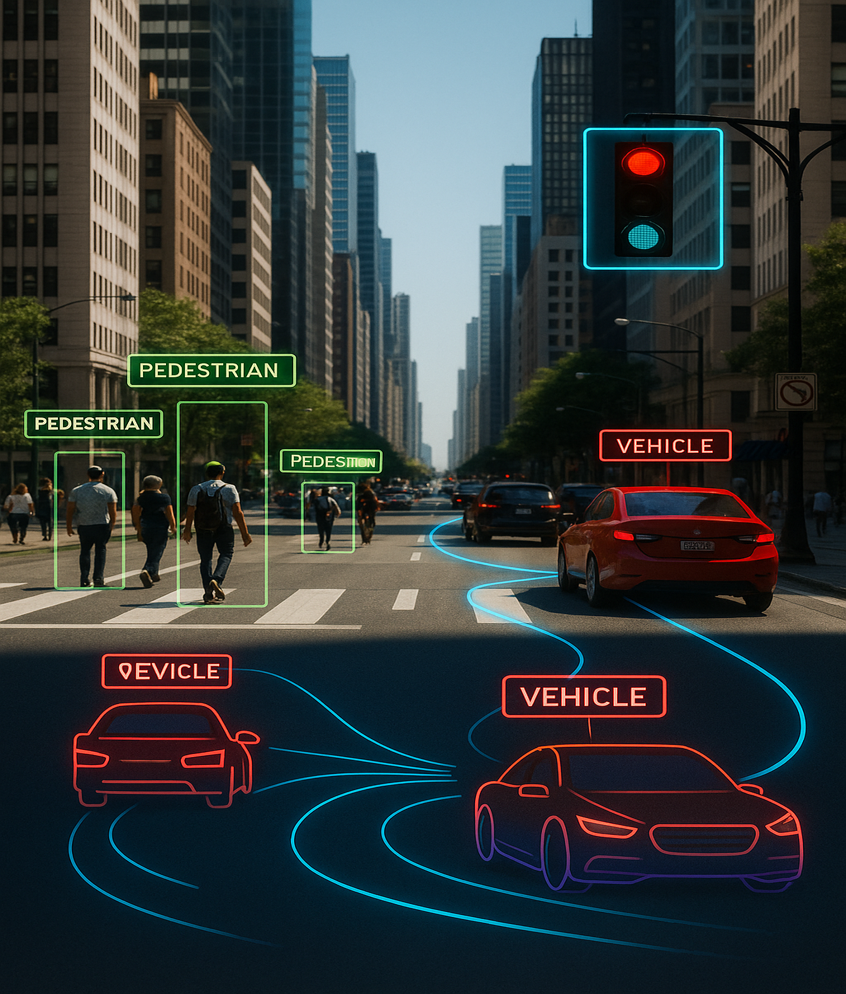
Computer Vision Systems
Detect, track, and classify with robust, real-time vision models.
Ready to transform your business with AI?
Let our team help you innovate faster with intelligent automation and generative AI solutions.
Contact UsDISCOVER YOUR FUTURE WITH US
Welcome to Tech AI, where we are revolutionizing the way businesses operate through cutting‑edge technologies and innovation. We are seeking ambitious and motivated employees who are passionate about the world of artificial intelligence and eager to learn from industry experts.
As an employee at our company, you will have the opportunity to work on real‑world projects alongside our experienced team of data scientists, engineers, and designers. You will gain hands‑on experience in developing and implementing AI solutions using the latest tools and techniques.

